When we speak of Mediterranean diet, we usually identify with this term Italy or Greece known for their life style and food habits but we must not forget that there are more than 15 other countries bordering the Mediterranean and that, although of different cultures, ethnic groups, religions, they have in common some characteristics that are:
|
|
High consumption of fruit, vegetables, potatoes, beans, walnuts, seeds, bread and cereals |
|
|
Use of olive oil for cooking and as condiment |
|
|
Moderate quantities of fish but little meat |
|
|
Moderate quantities of fat cheese and whole yogurt |
|
|
Moderate consumption of wine, usually at meals |
|
|
Diet based on fresh in season local products |
|
|
Active life style |
“Mediterranean Diet” is a word coined in the 60’s by Ancel Keys, an American researcher who, in the 50’s, after a long stay in the South of Italy, Campania, observed that the ratio between mortality and cause/death of the people living there, was very low for cardiovascular diseases. He carried out a study comparing the food habits of the United States, Italy, Greece, Yugoslavia, Holland, Finland, Japan. He and his equipe investigated on the food habits of 14.000 people aged 40-59 subdivided into 14 samples. From this study emerged that mortality for ischaemic cardiopaty was sharply inferior between the countries bordering the Mediterranean. Italy along with Greece and Japan was one of the three countries with the lowest incidence of cardiovascular diseases. Yet food habits were not uniform in Italy: in the South people ate more fruit,legumes, vegetables, fish, cereals and olive oil and less milk and by-products, meat, butter, eggs. The more the consumption of animal fat the higher the frequency of cardiovascular diseases was. The superior mortality of the other countries of the research were ascribed to the diet that included a higher amount of saturated fats such as lard, butter, red meat, confirmed also by further studies. Ancel Kyes had highlighted the benefits of the peasant’s diet on which Anglosaxon countries would have based the Food Pyramid.

Ø OLIVE OIL SOURCE OF HEALTH BENEFITS
Olive oil called by Homer “liquid gold” has been more than a mere food for the peoples of the Mediterranean basin. For centuries they have recognized the benefits of the olive oil in the field both of cosmetics and medicine.
|
|
It mainly consists of un-saturated fatty acids, such as oleic acid, which lowers the levels of LDL leaving HDLs free to clean the arteries |
|
|
It is rich in A, B1, B2, C, D, E, K vitamins and iron |
|
|
It contains antioxidants that discourage the clogging of arteries and chronic diseases as well as cancer |
|
|
It does not contain cholesterol |
|
|
It contains oleic acid necessary to balance the lipidic component in the diet |
|
|
Polyphenols found in the oil inhibit the growing rate of bacteria such as Salmonella, Cholerae, Staphylococcus and they are also used in the pharmaceutical industry to prevent skin damage due to an overexposure to the sun rays |
|
|
The leaf contain oleuropein a compound which acts as an antibiotic in the body, cleaning the system and reinforcing the immunitay system |

The “pitale” , an ancient oil container
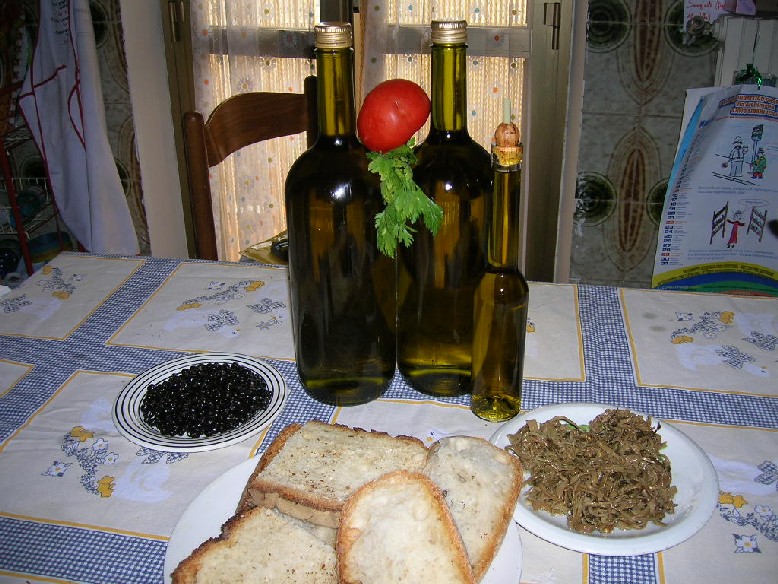

Olive Oli, with black olives, bread slices and "scapecia" (slises of eggplant in oil)
Ø OLEIC ACID AND OIL COMPOSITION
Oleic Acid is an organic fatty acid found in animal and vegetable oils and it is called a mono-unsaturated fatty acid because of the single double bond between the carbons.
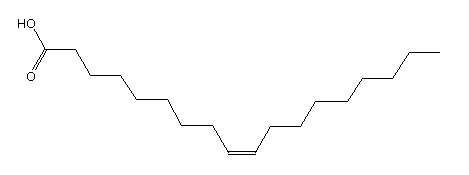 Structure of oleic acid
Structure of oleic acid
Its IUPAC name is cis-9-octadecenoic acid, and its lipid short name is 18:1 cis-9. Other names are: 9-Octadecenoic acid, (Z)-; oleic acid; (Z)-9-octadecenoic acid. It is a pale yellow or brownish yellow oily liquid with lard-like odour; insoluble in water; Melting Point 15.3 °C; Boiling Point 360 °C ; Specific Gravity 0.895.
With hydrogen addition, the double bond is satured and gives rise to the stearic acid.
 Stearic
acid structure
Stearic
acid structure
The organoleptic test is important to characterize the oil. As a matter of fact, there are preparatory courses for oil tasters and special places where to taste it.
Chemical analyses of the oil are useful to find its acidity, peroxides, spectrophotometric indexes, sterolic and acidic compositions.
Olive oil
is composed mostly of triglycerides (98 - 99%),
which comprise the most important fatty acids: oleic (65 -80%), linoleic (<13%)
and palmitic (7-15%) acids.
Rich in a right quantity of unsaturated fatty acids, it contains significant
quantities, but not less important, of beta-carotene
(provitamin A) and tocopherols (vitamin E), and fenolic compounds, very
important because they help to prevent the oil oxidation (rancid state of oil),
good nutritional benefits and it helps to prevent cell and
tissue damage that leads to disease
(free-radical antagonist). Phytosterols, present
in the oil, too, are very important because they have a regulatory function
for cholesterol absorption. Modern
studies have been claimed the benefits of consuming olive oil, since evidence
suggests that oleic acid helps lower levels of harmful low-density lipoproteins
(LDLs) in the bloodstream, while leaving levels of beneficial high-density lipoproteins
(HDLs) unchanged. Oleic acid is also found in significant quantities in
canola, cod-liver, coconut, soybean, and almond oils, used as condiment, too.
Calabria produces about 100.000 tons of olive oil and it is the second Italian
region as far as Oliveculture. Among the main
“cultivar” types there are the “Carolea”, the “Cassanese”, the “Dolce from Rossano”,
the “Sinopolese”, the “Ottobratica”, the “Roggianella” and the “Grossa from
Gerace”.
Ø THE FOOD PYRAMID
The Food Pyramid has been worked out by the United States Department of Agriculture upon information got by studies carried out by the researcher Ancel Keys on the Mediterranean diet and the low mortality rate for cardiovascular diseases giving the start to a campaign in order to guide American people towards the right choice and consumption of food to prevent cardiovascular risk.
One of the characteristics of the Mediterranean diet is to revalue a main course meal such as pasta with legumes, different types of minestrone, stew with potatoes, pizza to which it is sufficient to combine a plate of raw vegetables and fresh fruit to have a nutritionally balanced meal , which are also food utilized by the Italian traditional cooking and that make up the diet.
The food pyramid adjusted to the Mediterranean diet allows us to see the proportions and frequency of food intake which going from the bottom to the top are more and more reduced in terms of the average quantity for a correct diet.
|
|
At the base there are pasta, bread, rice, polenta, couscous, potatoes and it is recommended a big quantity, daily |
|
|
In the middle we find vegetables, fruit, legumes, dry fruit, olive oil, milk, cheeses, yogurt whose consumption should be daily |
|
|
Further up there are fish, poultry, eggs, recommended weekly or a few times a week |
|
|
At the top we have sweets and red meat whose consumption must be montly |
It is also recommended a steady physical activity and the consumption of moderate quantity of wine, especially red , since it is thought it helps to prevent tumor and cardiovascular diseases.

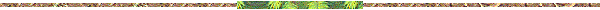
Ø THE NEW FOOD PYRAMID
The old Pyramid has lately been revised by the studies carried out by two authoritative American epidemiologists W. Willet and M. Stampfer. The new official Pyramid has some breaking points with the old one.
|
|
Not all fats have the same nutritional values |
|
|
The classic difference between simple and complex carbohydrates doesn’t enable the consumer to select the food with the best healthy values |
In the old Pyramid fats were placed at the top, now there are only saturated fats ( butter) whereas vegetable oils (olive oil, maize, canola) are found at the base of the pyramid; margarines,instead, are banned.
Complex carbohydrates (bread, pasta, rice) placed at the base are now found at the top whereas wholemeal cereals, rich in fibre, are at the base of the pyramid. The new location is due to the fact that wholegrain cereals are absorbed more slower by the body and more slower results the increasing of sugar rate in the blood .
The new pyramid has been integrated by an inferior hoof to underline the need of a daily physical activity and suggests also a moderate consumption of alcohol and a supplement of vitamins.
As for the Italian diet situation, people have always used olive oil and made little use of butter. A balanced intake of these two families of fats (monounsaturated, polyunsaturated) allows us to benefit of both specific nutritional values:
|
|
A major action of the control of cholesterolein typical of polyunsaturated fats like the linoleic acid, and at the same time the most favourable effect of monounsaturated on HDL cholesterol |
|
|
Antioxidants present in both oil groups (vitamin E, in the maize oil; polyfenolic antioxidants, oleuropein, in olive oil) make a potentially complementary antioxidant action |
As for the carbohydrates, the Italian pasta is prepared with durum wheat flour and cooked“ al dente” showing a low glycemic index and therefore it is one of the food to favour while it is thought that alcohol, taken in a moderate quantity (usually wine at meals) helps to reduce cardiovascular risk; as for the supplement of vitamins Italian diet makes large use of food rich in vitamins such as fresh fruit and fresh vegetables.
Ø GUIDELINES FOR A HEALTHY DIET
The INRAN (National Institute of Research for Food and Nutrition) recommends the following eating guidelines to keep a correct and balanced diet:
|
|
Eat lots of fruit and vegetables, ideally five portions |
|
|
Be wary of the amount of fat you eat |
|
|
Try to eat half of your daily food in the form of starchy carbohydrates such as pasta, potatoes, bread and rice |
|
|
Replace refined flour with wholemeal flour |
|
|
Eat more fibre- rich foods such as wholemeal bread and pasta, brown rice and pulses |
|
|
Cut down on sugar |
|
|
Cut down on salt |
|
|
Drink lots of water and reduce tea and coffee intake |
|
|
Cut down on sugary canned drinks and particularly on alcohol intake |
|
|
Vary your food choice as much as possible |
Origin and spread of olive tree in Itlaly Overweight and Obesity in Italy