Fundamental Stellar Parameters
Schmidt-Kaler Empirical Calibrations
Calibration of (B_V)o, MK spectral types from Schmid-Kaler 1982 various luminosity classes.
I apologize for the use of the Italian notation in the following tables. The commas should always be read as dots.
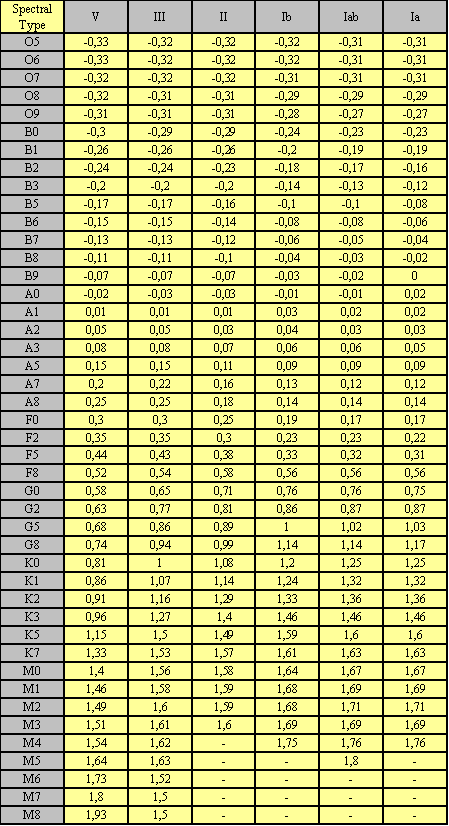
![]() Calibration of (U-B)o, MK spectral
types from Schmidt-Kaler various
luminosity classes
.
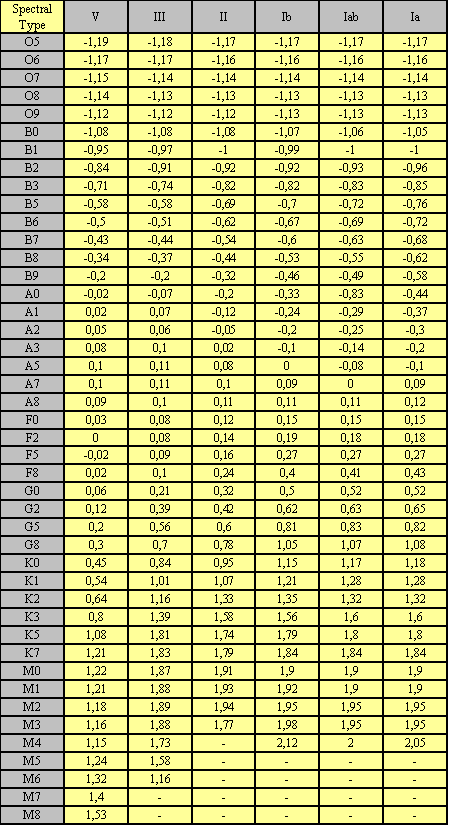
Calibration of (U-B)o, MK spectral
types from Schmidt-Kaler various
luminosity classes
.
![]() The ( Yerkes or ) MK system: spectral
type and luminosity class.
The ( Yerkes or ) MK system: spectral
type and luminosity class.
For a given chemical composition, a star spectrum is determined by the degree of ionization, temperature and electron pressure. All this features are taken into account in the Yerkes system through a second parameter namely: luminosity class (LC). Each luminosity class is subdivided into three subclasses namely: a, ab, b in oder of decreasing luminosity, see the following table.
LC |
Stars type |
Examples |
0
- 0Ia - Ia0 |
Super-supergiants |
G0 Ia-0 |
Ia
- Iab - Ib |
Supergiants |
B1 Iab |
IIa
- IIab - IIb |
Bright giants |
K0 II |
IIIa
- IIIab - IIIb |
Giants |
K0 IIIa |
IVa
- IVab - IVb |
Subgiants |
K2 IV |
Va
- Vab - Vb |
Main sequence
stars |
G2 V |
VI |
Subdwarfs |
sdK3 |
VIII |
White dwarf |
wAO, DB |
![]() Absolute Stars Magnitudes of the MK system ( Various Luminosity Classes ).
Absolute Stars Magnitudes of the MK system ( Various Luminosity Classes ).
LC |
V |
IV |
III |
II |
Ib |
Iab |
Ia |
Ia0 |
O3 |
-6,0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
-6,8 |
- |
O4 |
-5,9 |
-6,1 |
-6,5 |
- |
- |
- |
-6,8 |
- |
O5 |
-5,7 |
-6,0 |
-6,3 |
- |
- |
- |
-6,8 |
- |
O6 |
-5,5 |
-5,8 |
-6,1 |
- |
- |
-6,5 |
-6,8 |
- |
O7 |
-5,2 |
-5,5 |
-5,9 |
-6,0 |
-6,3 |
-6,5 |
-6,8 |
- |
O8 |
-4,9 |
-5,4 |
-5,8 |
-6,0 |
-6,2 |
-6,5 |
-6,8 |
- |
O9 |
-4,5 |
-5,2 |
-5,6 |
-5,9 |
-6,2 |
-6,5 |
-6,8 |
- |
B0 |
-4,0 |
-4,7 |
-5,1 |
-5,7 |
-6,1 |
-6,4 |
-6,9 |
-8,2 |
B1 |
-3,2 |
-3,8 |
-4,4 |
-5,4 |
-5,8 |
-6,4 |
-6,9 |
-8,3 |
B2 |
-2,45 |
-3,1 |
-3,9 |
-4,8 |
-5,7 |
-6,4 |
-6,9 |
-8,3 |
B3 |
-1,6 |
-2,4 |
-3,0 |
-4,5 |
-5,5 |
-6,3 |
-7,0 |
-8,3 |
B5 |
-1,2 |
-1,7 |
-2,2 |
-4,0 |
-5,4 |
-6,2 |
-7,0 |
-8,4 |
B7 |
-0,6 |
-1,1 |
-1,5 |
-3,5 |
-5,3 |
-6,2 |
-7,1 |
-8,4 |
B8 |
-0,25 |
-0,7 |
-1,2 |
-3,1 |
-5,2 |
-6,2 |
-7,1 |
-8,5 |
B9 |
+ 0,2 |
-0,2 |
-0,6 |
- |
-5,2 |
-6,2 |
-7,1 |
-8,5 |
A0 |
+ 0,65 |
+0,3 |
0,0 |
-3,0 |
-5,2 |
-6,3 |
-7,1 |
-8,5 |
A1 |
+ 1,0 |
+0,7 |
+0,2 |
-3,0 |
-5,2 |
-6,4 |
-7,2 |
-8,5 |
A2 |
+ 1,3 |
+1,0 |
+0,3 |
-2,9 |
-5,2 |
-6,5 |
-7,2 |
-8,6 |
A3 |
+ 1,5 |
+1,2 |
+0,5 |
-2,8 |
-5,2 |
-6,5 |
-7,2 |
-8,7 |
A5 |
+ 1,95 |
+1,3 |
+0,7 |
-2,8 |
-5,1 |
-6,6 |
-7,4 |
-8,8 |
A7 |
+2,2 |
+1,7 |
+1,1 |
-2,7 |
-5,1 |
- |
-7,7 |
-8,9 |
A8 |
+2,4 |
+2,0 |
+1,2 |
-2,6 |
-5,1 |
- |
-7,8 |
-8,9 |
F0 |
+2,7 |
+2,2 |
+1,5 |
-2,5 |
-5,1 |
-6,6 |
-8,0 |
-9,0 |
F2 |
+3,6 |
+2,4 |
+1,7 |
-2,4 |
-5,1 |
-6,6 |
-8,0 |
-9,0 |
F5 |
+3,5 |
+2,5 |
+1,6 |
-2,3 |
-5,1 |
-6,6 |
-8,0 |
-9,0 |
F8 |
+4,0 |
+2,8 |
- |
-2,3 |
-5,1 |
-6,5 |
-8,0 |
-9,0 |
G0 |
+4,4 |
+3,0 |
+1,0 |
-2,3 |
-5,0 |
-6,4 |
-8,0 |
-8,9 |
G2 |
+4,7 |
+3,0 |
+0,9 |
-2,3 |
-5,0 |
-6,3 |
-8,0 |
-8,8 |
G5 |
+5,1 |
+3,1 |
+0,9 |
-2,3 |
-4,6 |
-6,2 |
-7,9 |
-8,6 |
G8 |
+5,5 |
+3,1 |
+0,8 |
-2,3 |
-4,4 |
-6,1 |
-7,8 |
-8,5 |
K0 |
+5,9 |
+3,1 |
+0,7 |
-2,3 |
-4,3 |
-6,0 |
-7,7 |
-8,5 |
K1 |
+6,15 |
+3,1 |
+0,6 |
-2,3 |
-4,3 |
-6,0 |
-7,6 |
- |
K2 |
+6,4 |
- |
+0,5 |
-2,3 |
-4,3 |
-5,9 |
-7,6 |
- |
K3 |
+6,65 |
- |
+0,3 |
-2,3 |
-4,3 |
-5,9 |
-7,5 |
- |
K4 |
+7,0 |
- |
0,0 |
-2,3 |
-4,3 |
-5,8 |
-7,5 |
- |
K5 |
+7,35 |
- |
-0,2 |
-2,3 |
-4,4 |
-5,8 |
-7,5 |
- |
K7 |
+8,1 |
- |
-0,3 |
-2,3 |
-4,4 |
-5,7 |
-7,4 |
- |
M0 |
+8,8 |
- |
-0,4 |
-2,5 |
-4,5 |
-5,6 |
-7,0 |
-8,0 |
M1 |
+9,3 |
- |
-0,5 |
-2,5 |
-4,6 |
-5,6 |
-7,0 |
-8,0 |
M2 |
+9,9 |
- |
-0,6 |
-2,6 |
-4,7 |
-5,6 |
-6,9 |
-8,0 |
M3 |
+10,4 |
- |
-0,6 |
-2,6 |
-4,8 |
-5,6 |
-6,9 |
-8,0 |
M4 |
+11,3 |
- |
-0,5 |
-2,6 |
-4,8 |
-5,6 |
-6,8 |
-8,0 |
M5 |
+12,3 |
- |
-0,3 |
- |
-4,8 |
-5,6 |
-6,8 |
- |
![]() Calibrations of special luminosity criteria.
Calibrations of special luminosity criteria.
- The Mv(b) calibration
b |
Mv(b) |
2,560 |
-6,51 |
2,570 |
-5,84 |
2,580 |
-5,22 |
2,590 |
-4,65 |
2,600 |
-4,12 |
2,610 |
-3,62 |
2,620 |
-3,17 |
2,630 |
-2,75 |
2,640 |
-2,36 |
2,650 |
-2,01 |
2,660 |
-1,69 |
2,670 |
-1,39 |
2,680 |
-1,12 |
2,690 |
-0,87 |
2,700 |
-0,65 |
2,710 |
-0,45 |
2,720 |
-0,27 |
2,730 |
-0,10 |
2,740 |
+0,04 |
2,750 |
+0,18 |
2,760 |
+0,30 |
2,770 |
+0,41 |
2,780 |
+0,51 |
2,790 |
+0,60 |
2,800 |
+0,68 |
2,810 |
+0,76 |
2,820 |
+0,83 |
2,830 |
+0,90 |
2,840 |
+0,97 |
2,850 |
+1,03 |
2,860 |
+1,10 |
2,870 |
+1,17 |
2,880 |
+1,24 |
2,890 |
+1,31 |
2,900 |
+1,39 |
![]() Effective
temperatures, bolometric corrections and luminosities.
Effective
temperatures, bolometric corrections and luminosities.
- Bolometric correction -
Log(Teff) |
Teff [K] |
BV lc V |
BC lc III |
BC lc I |
4,9 |
79000 |
-6,15 |
-6,15 |
-6,15 |
4,8 |
63000 |
-5,35 |
-5,35 |
-5,35 |
4,7 |
50000 |
-4,60 |
-4,60 |
-4,60 |
4,6 |
40000 |
-3,83 |
-3,83 |
-3,83 |
4,5 |
31600 |
-3,23 |
-3,09 |
-3,09 |
4,4 |
25100 |
-2,67 |
-2,52 |
-2,39 |
4,3 |
20000 |
-2,16 |
-1,97 |
-1,77 |
4,2 |
15900 |
-1,52 |
-1,40 |
-1,20 |
4,1 |
12600 |
-0,92 |
-0,85 |
-0,82 |
4,0 |
10000 |
-0,37 |
-0,37 |
-0,45 |
3,9 |
7940 |
-0,13 |
-0,13 |
0,00 |
3,8 |
6310 |
-0,15 |
-0,14 |
-0,03 |
3,7 |
5010 |
-0,38 |
-0,36 |
-0,27 |
3,6 |
3980 |
-1,11 |
-0,97 |
-0,85 |
3,55 |
3550 |
-1,97 |
-1,82 |
-1,45 |
3,5 |
3160 |
-2,97 |
-3,00 |
-2,22 |
3,45 |
2820 |
-3,71 |
-3,71 |
-3,38 |
3,4 |
2510 |
-4,4 |
-4,4 |
-4,1 |
3,3 |
2000 |
-6,1 |
-6,1 |
-6,1 |
3,2 |
1600 |
-8 |
-8 |
-8 |
- Photometry references-
The reader can find many others data on previous arguments in:
© 2006 - Valter Arnò